Looking for something else?
Titan – AN18: Web Control and Data Collection Platform for Routers and Modems with Tunnel
Table of Contents
Introduction
Titan routers and modems with MTX-Tunnel firmware have the ability to send data to web platforms. Data that can be collected from sensors, but also own data, such as IP address, coverage, firmware version, etc. It is also possible to communicate with them from a web platform to execute actions, such as a configuration change or the execution of a reset.
This application note is intended to be a utility for those users who want to build a small web platform for collecting data or simply monitoring their own equipment.
Data Transmission of the Titan Routers and MTX-Tunnel Modems
Titan routers and MTX-Tunnel modems have 2 types of data transmission. On the one hand the data of own state (IP, coverage, …). On the other hand the data of your internal datalogger. Both types of data can be sent via HTTP or HTTPS to the web platform.
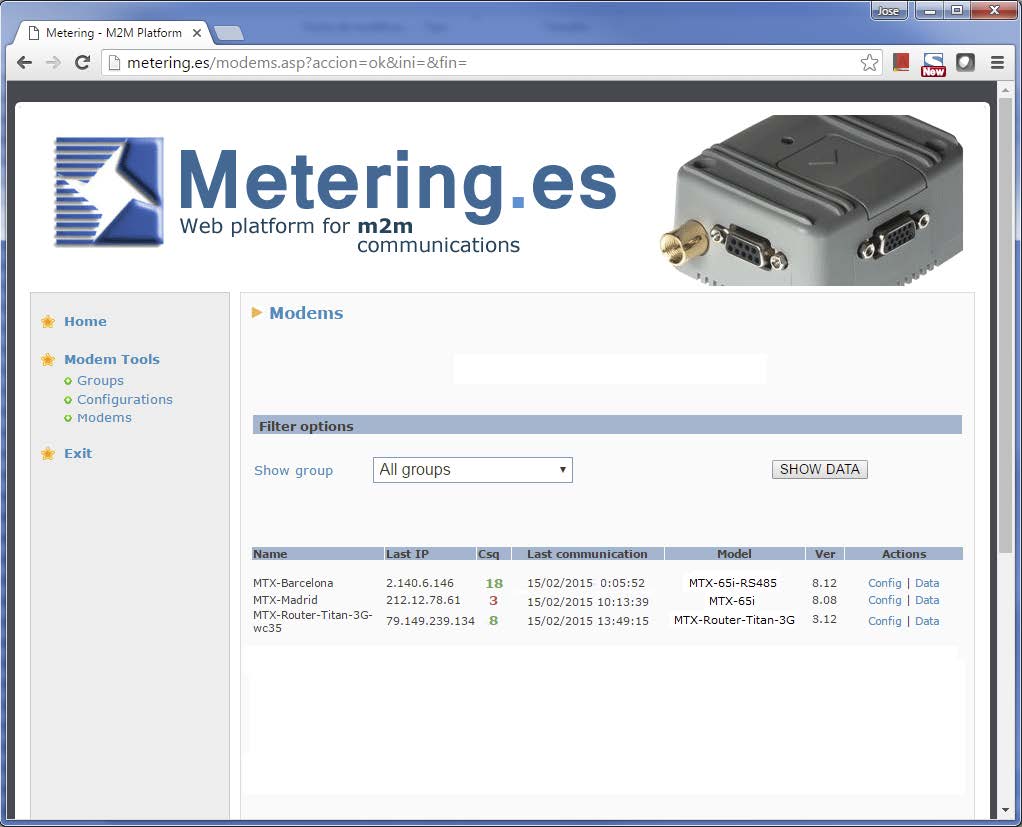
Imagine that we want to make a simple web page showing a list of MTX devices that we have installed in the field. In this page we will show, for each MTX, its name, its current IP address, the GSM coverage level (rssi/csq), the date and time of the last MTX communication with the platform, the MTX model and The firmware version.
That is, we will configure the Titan routers and modems with MTX-Tunnel firmware so that periodically (or whenever they change their IP address) they communicate with a web platform to report on their status. As an example, we want to design a web page like the one shown in the following figure:
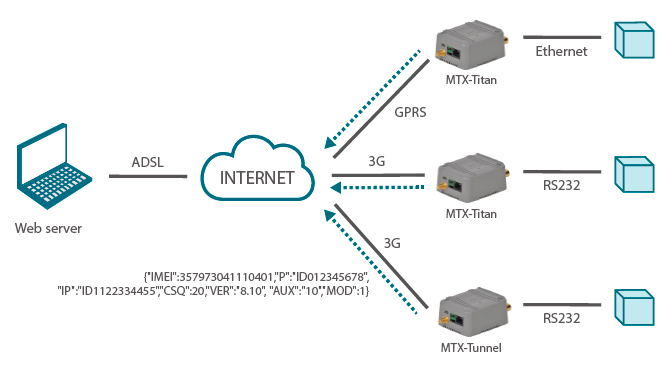
Modems with MTX-Tunnel firmware and Router Titan can send their status data to a Web Platform via HTTP GET/HTTPS GET. In both cases the encapsulated data can be sent to a JSON object, which simplifies the use of the same as it allows the scalability for new data sent in future firmware versions.
Status data sent by Modems with MTX-Tunnel firmware and Router Titan are very similar.
Example of Sending Status Data from a Modem with MTX-Tunnel Firmware:
{IMEI:357973041110401,P:ID012345678,IP:ID1122334455,CSQ:20,VER:8.10, AUX:10,MOD:1}
Where:
IMEI: internal identification of the MTX
P: KEYID of the device defined in the DNS_password parameter
IP: Current MTX IP
CSQ: MTX gsm coverage (0 … 31)
VER: MTX-Tunnel firmware version
AUX: CustomData
MOD: MTX Modem Model
Example of Sending Status Data from a Router Titan:
{TYPE:DNS,IMEI:357044060009633,IP:95.126.36.167,P:ID12345678,RSSI:16,MOD:101,VER:3.00.3.15}
Where:
TYPE: Indicates the type of information sent
IMEI: internal identification of the MTX
P: KEYID of the device defined in the DNS_password parameter
IP: Current MTX IP
RSSI: MTX gsm coverage (0 … 31)
VER: MTX-Tunnel firmware version
MOD: MTX Modem Model
Configuration of the Titan Router to Send Status Data to the Web Platform
Setting up a Titan router to periodically send your status data to a Web Platform is very simple. Just go to the configuration menu Other> Private DynDNS and configure the router in a similar way to the following figure:

That is, we activate the Enabled box, specify the HTTP GET mode, indicate the complete URL where to dump the data (without http/https), such as “www.metering.es/json/set.asp? Data =, and then in the field ID we can indicate the KEYID of the device. This will be used by the platform to identify the device. In the field Period we indicate the period (in minutes) of sending status data to the Web Platform. Remember that in case of a change of IP in the Router will also make a sending of status data, informing your new IP immediately.
With the data configured in the previous screen, the Titan router, every 60 minutes, will send its status data to www.metering.es/json/set.asp?data=, that is, from the data variable we will retrieve The JSON object with the status data.
Configuration of Modems with MTX-Tunnel to Send Status Data to Web Platform
The configuration of a Modem with MTX-Tunnel firmware is also very simple, but instead of making the configuration graphically it is done in the usual way MTX-Tunnel, that is, through a configuration file named config. Txt . It would be enough to add the following lines to the configuration file:
Where,
DNS_enabled on indicates that the status data must be sent periodically
DNS_mode http indicates that the HTTP GET method must be used
DNS_httpMode json indicates that the data sent must have the format JSON
DNS_server indicates the full URL to where we want to send the data
DNS_period specifies the period (in seconds) of sending status data
DNS_aux: can be used for sending user data
DNS_extended: off we indicate that we do not want to send us the digital and analog I/O.
If we wanted the modem to enter in the JSON such data we would put on
With this configuration, the Modem with MTX-Tunnel firmware will send its status data to the www.metering.es/json/set.asp?data= every 1800 seconds (30 minutes).
Send Data from Web Platform to a Router or Modem with MTX-Tunnel Firmware
At this point we would be ready to create a Web Platform for collecting the status of remote devices. Something like the one shown below. Whit this, we can list that information from the data received periodically from each device, that is, its last IP, the coverage value, etc.
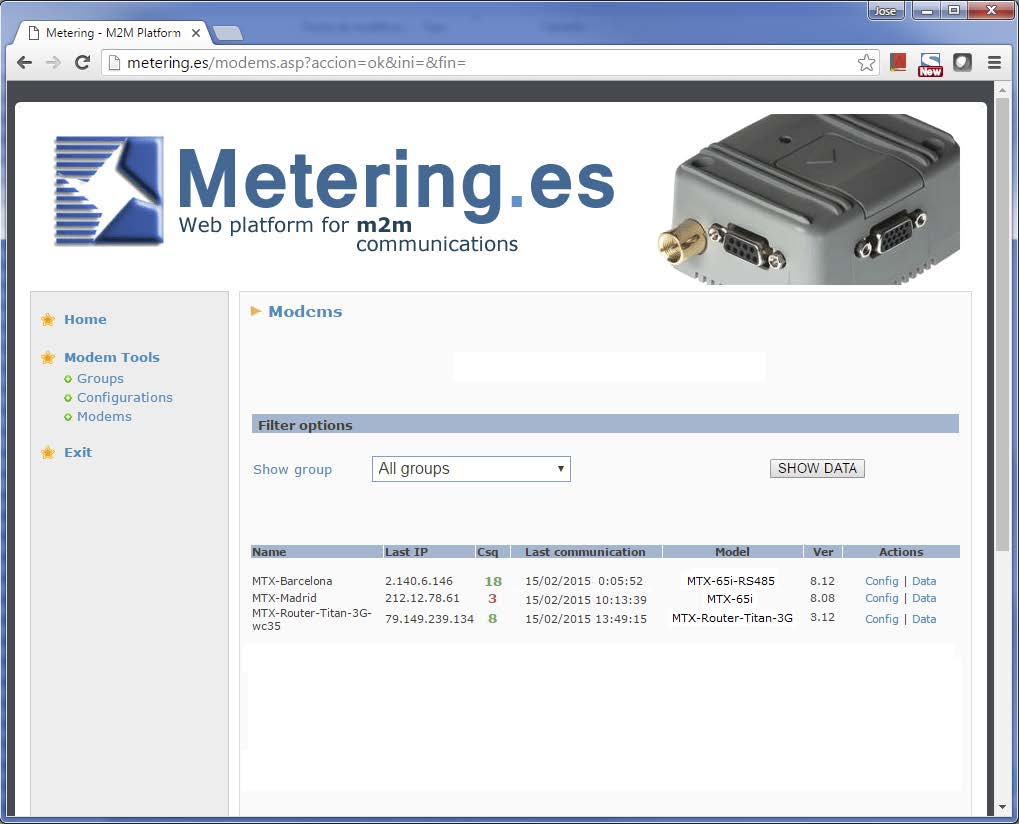
This is great, we can see the status of our remote devices in real time, detect problems (communication, low coverage, etc.). But we may need to take some action on the Modem / Router from the web platform itself. Imagine that we want to commute a relay, how would we do it?
Both the Titan Router and the Modems with MTX-Tunnel firmware have their own API to perform certain actions. This API basically consists of a set of AT commands. If you are a user of the Titan Router and modems with signature MTX-Tunnel you will know that these AT commands can be sent to the modem in many ways depending on the device: TCP socket, Telnet, HTTP GET, SMS, RS232 / 485, Modbus TCP, SNMP… Refer to the user manual to discover all AT commands available on each platform as well as how to use them.
For the present example we will focus on the commands:
AT^SSIO=0,0 It allows to activate a digital output in a modem with MTX-Tunnel
AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETRELAY,0,1 It allows to activate the internal relay of the Titan router
We want to switch the modem digital output or the Router Titan relay from the web. The web would only have to send, in response to an HTTP GET sending of the Modem/Router, something as simple as:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^SSIO=0,0</MTXTUNNELR> for MTX-Tunnel
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETRELAY,0,1</MTXTUNNELR> for Titan
That easy. As soon as the Modem or Router connects to the platform to send data, the web platform will send this command and we will be able to observe how the relay switches.

Change the Complete Configuration of MTX-Tunnel Modem from the Web Page
There are several ways to change the configuration of a MTX-Tunnel modem from a web platform. The procedure would be exact to previous example of the switching of a relay. The only change we have to make is the AT command itself. In this case, the response command we would send would be:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETCONFIG, COMM_baudrate: 115200 COMM_bitsperchar: 8 …. …. DNS_AUX: 11 TELNET_enabled: on TELNET_login: user TELNET_password: 1234 CSD_enabled: off </MTXTUNNELR>
Once this is done, the modem will reboot automatically and we would have the new configuration.
How can we know the configuration version that has a certain MTX-Tunnel modem so that the web platform can decide whether to update its configuration or not to update it?
A simple way is to use the DNS_AUX configuration parameter. Recall, as indicated in the first pages of this application note, each time the MTX-Tunnel modem communicates with the web platform sends an AUX parameter:
{IMEI:357973041110401,P:ID012345678,IP:ID1122334455,CSQ:20,VER:8.10, AUX:10,MOD:1}
This parameter corresponds to the DNS_AUX value of the configuration file config.txt. For example, if we receive the AUX parameter of the MTX-Tunnel modem with a value of 10 and it does not match the one of the platform (imagine that the current configuration version is 11), we will make the web platform send the New configuration to the MTX-Tunnel. Obviously the new configuration sent to the modem would contain the DNS_AUX: 11 field.
As a schematic:
The modem with MTX-Tunnel firmware sends its status periodically. The AUX field returns a value of 10 because in its configuration file the DNS_aux parameter is 10.

The Web Platform detects that the 10 configuration is obsolete and sends a new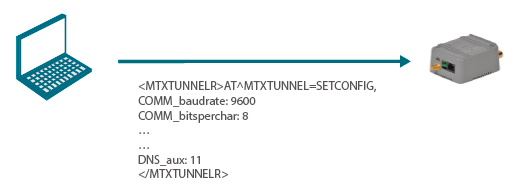 configuration, in which the DNS_aux parameter will be 11.
configuration, in which the DNS_aux parameter will be 11.
Send AC Commands to Devices with MTX-Tunnel in Real Time
We have shown how to build a small web control platform that allows us to periodically receive the status of modems and routers and perform an action on them every time a communication is received.
In other scenarios it may be necessary to perform an action on a modem/router at any given time, without having to wait for the modem to communicate with the Web Platform. For this, the MTX Tunnel Modems and the Router Titan incorporate a special configuration. This configuration causes these devices to open a TCP socket permanently against the IP address (or DNS) of the Web Platform to a certain TCP port. By means of this permanent TCP connection we can send AT commands to the MTXTunnel Modem and Router Titan at any time, that is, to execute actions in real time.
In this case we will have to develop a web page that supports sockets server. This is a page php, asp. net, java… that allows to manage these connections coming from each team. In this application note will not enter the programming of the website, but in the appropriate configuration of the Modems MTXTunnel and Router Titan to be able to establish such communication channel in real time.
Router Configuration to Receive Commands Sent from Web Platform in Real Time
In order to send commands in real time to a Titan router from a web platform we must configure a TCP communication socket on the router that will be permanently established against the platform. To do this we must configure the router Titan in the following way.
Other > Console menu and configure the different parameters in the same way as the following figure:

That is, we activated the console in TCP Client mode (connection FROM THE modem TOWARDS the Web Platform). We indicate the IP address (dns) and TCP port to where we want to connect the Router Titan, a KEYID with which the TITAN router will be identified in the Web Platform and a retry period. That is, a pause time after which, in case of fall of the socket, the connection is again retried.
The KEYID is the first thing that the Titan Router will transmit through the socket once established. It must be used by the Web Platform to identify the remote computer and accept or not a connection.
Once the LINK is established it is possible to send any command to the modem. For example, if at any given moment we want a Router Titan to initiate an OpenVPN connection against another router, we could send a command to open a 10-minute client OpenVPN session against IP 1.2.3.4 and port 1194:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=OVPNX,10,1.2.3.4,1194</MTXTUNNELR>
To activate Relay 1 of the Titan Router:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETRELAY,0,1</MTXTUNNELR>
To reset the Titan router:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=REBOOT</MTXTUNNELR>
To change the baudrate configuration of the COM1 serial port of the router:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETPARAM,COM1_BAUDRATE, 9600</MTXTUNNELR>
To read from the platform the baudrate configuration of the COM1 serial port of the router:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETPARAM,COM1_BAUDRATE</MTXTUNNELR>
Etc.
Modem Configuration to Receive Commands Sent from Web Platform in Real Time
In order to send real-time commands from our Web Platform to a MTX-Tunnel Modem we must configure a TCP communication socket on the modem that will be permanently established against the Web Platform. To do this, we must configure the MTX-Tunnel Modem as follows, analogously including the following configuration lines in the file config.txt.
Where:
LINK_enabled on indicates that we want to set the LINK for real-time control
LINK_ip IP or DNS of the Web Platform
LINK_port TCP Port of the Web Platform to which the modem will connect
LINK_retryPeriod indicates the pause seconds before resetting the socket, in case of fall
LINK_timeout indicates seconds to reset socket in the absence of data transfer in the socket
LINK_ keyId identifying string the modem will send to the web platform for identification
Once the LINK is established it is possible to send any command from the Web Platform to the MTXTunnel Modem. For example, if at any given time we want to know the GSM coverage of the modem, it would be enough to send from the Web Platform the command and we would get the GSM coverage level of the modem at that moment:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT+CSQ</MTXTUNNELR>
To read from the web platform the status of all the digital and analog inputs of the modem:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETIOS</MTXTUNNELR>
To change the baudrate of the modem\’s main port to 9600 baud:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETPARAM,COMM_baudrate,9600</MTXTUNNELR>
To read the configuration of the baudrate parameter of the main port of the modem:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=GETPARAM,COMM_baudrate</MTXTUNNELR>
To reset the modem:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT+CFUN=1,1</MTXTUNNELR>
To activate the digital relay1 (or digital output):
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=SETIO,0,0</MTXTUNNELR>
To read the temperature stirred by the Wavenis Radio sensor with MAC 1A2356764511:
<MTXTUNNELR>AT^MTXTUNNEL=READWAVETHERM,1A2356764511</MTXTUNNELR>
Etc.
Collecting Data from Modems with MTX-Tunnel and Titan Routers
Both Modems with MTX-Tunnel firmware and the Titan Routers are able to send data from sensors that they collect themselves autonomously. Temperature sensors, pulse counters, analog inputs, generic serial devices, etc.
In the same way as sending status data, the sending of sensor data is done by sending a JSON object. Refer to the MTX-Tunnel or Titan Routers general manual for more information on the JSON object parameters for each type of sensor.



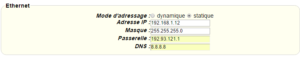
 Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
Enter the “ethernet” or “modem” connection type:
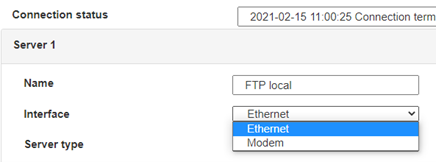 For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
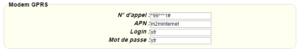
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
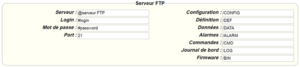
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
For an ethernet configuration, make sure the IP parameters are compatible with server access according to the concentrator local network configuration. For an ethernet connection, the configuration must be compatible with the concentrator’s local network topology so that it can access the servers. This configuration is done from the “Networks” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.3: “Networks”).
For a modem connection, the modem configuration must be correct before a connection can be set up. This configuration is done from the “Modem” configuration page (see section 3.2.2.4: “Modem”).
The parameters for the servers to be configured are at least the following:
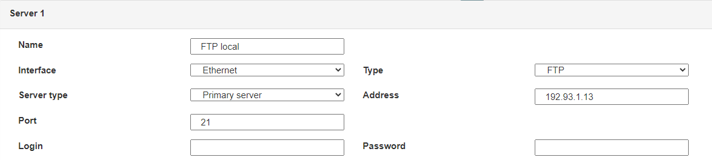 Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.
Therefore the following fields need to be configured: “Interface”, “Type”, “Server type”, “Address”, “Port”, “Login” and “Password”.
The other fields can be left at the default values subject to the directories having been properly created beforehand. See section 3.1.2: “Configuration files” for more details.



 Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.
Wait. The concentrator will reboot using its factory configuration.